Archive
Microsoft Dynamics CRM – Windows Server & SQL Server Supported Versions
This post will provide a quick snapshot of the supported versions of Windows Server and SQL Server for Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011. This posting will also be a quick reference post for me in the future.
Windows Server
The following Microsoft Windows Server editions and versions are supported for running Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011
- Windows Server 2012 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2012 Standard
- Windows Server 2008 Standard SP2 (x64 versions) or Windows Server 2008 Standard R2
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise SP2 (x64 versions) or Windows Server 2008 Enterprise R2
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter SP2 (x64 versions) or Windows Server 2008 Datacenter R2
- Windows Web Server 2008 SP2 (x64 versions) or Windows Web Server 2008 R2
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 Premium x64
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 Standard x64
- Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard
- Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials
- Note:
Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 Update Rollup 13 or a later is required with Windows Server 2012. Update Rollup 13 will also require Update Rollup 6 to be installed first.
- Windows Server 2008 installed by using the Server Core installation option is not supported for installing and running Microsoft Dynamics CRM Server 2011. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based systems is not supported for installing and running Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011.
SQL Server
The following Microsoft SQL Server editions and versions are supported for running Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008, Standard Edition, x64 SP1 or R2
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008, Enterprise Edition, x64 SP1 or R2
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Datacenter x64 SP1 or R2
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Developer x64 SP1 or R2 (for non-production environments only)
- *Microsoft SQL Server 2012, Enterprise, 64-bit
- *Microsoft SQL Server 2012, Business Intelligence, 64-bit
- *Microsoft SQL Server 2012, Standard, 64-bit
Note:
Microsoft Dynamics CRM Update Rollup 6 or later update rollup is required to use Microsoft SQL Server 2012.
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 and Microsoft SQL Server 2005 editions and are not supported by Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011.
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Workgroup, Web, Compact, or Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Express Edition editions are not supported for running Microsoft Dynamics CRM Server 2011.
32-bit (x86) versions of SQL Server database engine or Reporting Services are not supported with Microsoft Dynamics CRM Server 2011.
Greg Olsen
YellowDuckGuy
T-SQL – Read XML from a SQL Column Example
Below is a post to show you how you can read XML data which is held within a SQL table column using T-SQL. In my example below, the SQL column I had to read from was also not held in a XML data type. Therefore the column holding the XML data had to be converted to XML to take advantage of the XML functions.
Firstly, lets take a look at the column which has the XML data. Below it is shown in a column called VEHI.
What does this XML look like?
<BasicVehicleType xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<VehicleSystemId xmlns="http://localhost/Schema/CdiCommonTypes">11438229
</VehicleSystemId>
<YearOfManufacture xmlns="http://localhost/Schema/CdiCommonTypes">2002
</YearOfManufacture>
<Make xmlns="http://localhost/Schema/CdiCommonTypes">TOYOTA</Make>
</BasicVehicleType>
When I looked into the data type of this column I noticed that it is not XML but a varchar data type. Therefore I recommend converting this to the XML data type first to take use of the XML functions.
To convert the VEHI column to XML, we simply can use the CAST keyword. The T-SQL would look something like the following:
SELECT TOP 1 CAST(VEHI AS XML) AS VEHI
FROM LTSAQueries
WHERE VEHI IS NOT NULL
Hope this helps you when playing around with XML SQL data. If you have better options for dealing with XML than I have outlined here, then feel free to post a comment and let me know.
Greg Olsen
YellowDuckGuy
Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 – Database cannot be started in this edition of SQL Server
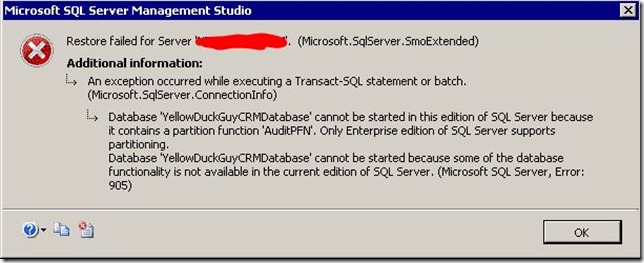
This article outlines what is required to repair the AuditPFN or Database cannot be started in this edition of SQL Server’ errors respectively.
If you try and restore a CRM 2011 database organisation from SQL Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition instance to a SQL Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition, then you will most likely hit the error shown below.
What does this mean?
When CRM 2011 is installed using the SQL Server Enterprise Edition, then a partition is created for the auditing functionality built in CRM 2011. The AuditBase table within CRM 2011 uses partitioning which is only available within SQL Server Enterprise Edition. If you then try and restore a backup of the database from SQL Server Enterprise Edition and restore it within SQL Server Standard Edition , then it will not start because SQL Server Standard Edition doesn’t support partitioning.
The fix/change Required
What you will need to do is use a T-SQL script to remove the partitioning from the backup SQL database. Follow the steps below to fix this issue.
1. Restore the ‘<yourcrmorgname>_MSCRM’ database to a server running Microsoft SQL Server Enterprise Edition.
2. Run the following script against the restored database. This script recreates all the indexes on the primary partition and then drops the partition.
Note: Don’t use your production or live database! Use a test server for this.
IF EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.partition_schemes WHERE name=‘AuditPScheme’)
BEGIN
SELECT
CASE WHEN ind.type != 1
THEN
‘DROP INDEX [dbo].[AuditBase].’ + QUOTENAME(ind.name) + ‘ ‘
ELSE ‘ ‘
END +
‘CREATE ‘ + CASE is_unique WHEN 1 THEN ‘UNIQUE ‘ ELSE ” END +
ind.type_desc + ‘ INDEX ‘ + QUOTENAME(ind.name COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS ) + ‘ ON [dbo].’ + QUOTENAME(OBJECT_NAME(object_id)) + ‘ (‘ +
REVERSE(SUBSTRING(REVERSE((
SELECT name + CASE WHEN sc.is_descending_key = 1 THEN ‘ DESC’ ELSE ‘ ASC’ END + ‘,’
FROM
sys.index_columns sc
JOIN sys.columns c ON sc.object_id = c.object_id AND sc.column_id = c.column_id
WHERE
OBJECT_NAME(sc.object_id) = ‘AuditBase’ AND
sc.object_id = ind.object_id AND
sc.index_id = ind.index_id
ORDER BY index_column_id ASC
FOR XML PATH(”)
)), 2, 8000)) + ‘)’ +
CASE WHEN ind.type = 1
THEN
‘ WITH (DROP_EXISTING = ON) ON [PRIMARY]’
ELSE
‘ ‘
END as Script
INTO #indexesScript
FROM sys.indexes ind
JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps on ind.data_space_id=ps.data_space_id
WHERE
OBJECT_NAME(object_id) = ‘AuditBase’
AND ps.name = ‘AuditPScheme’
AND is_unique_constraint = 0
SELECT * FROM #indexesScript
DECLARE @recreateScript nvarchar(max)
DECLARE indScript CURSOR FOR
SELECT Script FROM #indexesScript
OPEN indScript
FETCH NEXT FROM indScript INTO @recreateScript
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
BEGIN TRANSACTION t1
Execute sp_executesql @recreateScript
IF @@ERROR > 0
BEGIN
ROLLBACK TRAN t1
declare @message varchar(max)
set @message = ‘Audit history recreate index failed. SQL: ‘ + @recreateScript
RAISERROR (@message, 10,1)
END
ELSE
BEGIN
COMMIT TRAN
END
FETCH NEXT FROM indScript INTO @recreateScript
END
DROP PARTITION SCHEME AuditPScheme
DROP PARTITION FUNCTION AuditPFN
CLOSE indScript
DEALLOCATE indScript
DROP TABLE #indexesScript
END
3. Once you have run the script (as shown above), you can backup the database.
4. Restore the database from step 3 to a server running Microsoft SQL Server Standard edition. This database should now restore with no errors (AuditPFN issue is gone) and start correctly.
Hope this helps?
Greg Olsen
Yellow Duck Guy
CRM 4.0 & 2011 – SQL Code to show where your Plug-ins are registered
When you register your plug-ins for Microsoft Dynamics CRM 4.0 or 2011 you either choose to register to Disk, Database or the GAC. I always prefer the database option so my CRM system is altogether and easier to move with deployments if required.
When you use the Plug-in Registration Tool, the action you choose will be written to the Microsoft CRM SQL Database. Therefore we can write T-SQL to give us that information.
Below is the T-SQL you can use to tell you where your Plug-ins are registered. This works for CRM 4.0 and CRM 2011.
SELECT Name,
CASE SourceType
WHEN 0 THEN ‘Database’
WHEN 1 THEN ‘Disk’
WHEN 2 THEN ‘GAC’
END AS ‘Registered Location’
FROM PluginAssembly
Output shown below from CRM 2011 SQL Database
Yellow Duck Guy
How do I know which version of SQL Server I’m running?
To determine which version of Microsoft SQL Server 2005 or 2008 you are running, connect to SQL Server 2005 or 2008 by using SQL Server Management Studio, and execute the following T-SQL.
I have executed 3 T-SQL options:
- select @@version
- select SERVERPROPERTY (‘productversion’)
- select SERVERPROPERTY (‘productlevel’)
- select SERVERPROPERTY (‘edition’)
Greg Olsen
Yellow Duck Guy
Find a Column Name within your SQL Tables
SELECT tab.name AS TableName,
col.name AS ColumnName
FROM dbo.sysobjects tab
INNER JOIN dbo.syscolumns col
ON tab.id = col.id
WHERE tab.xtype = ‘U’ — User Table
AND col.name LIKE ‘%geek%’ — Column Name you’re looking for.
ORDER BY tab.name
Greg Olsen
Yellow Duck Guy
Refresh All Views in Database with T-SQL
This is a handy little piece of code I wrote, which can help if you ever need to refresh your database views within SQL Server. I have tested this on SQL Server 2005 recently. I have also had a SQL Job run this stored procedure to update my views more frequently. I had used this to keep views up-to-date for database integration projects.
1: CREATE Procedure dbo.RefreshAllViews
2: AS
3:
4: DECLARE @ViewName nvarchar(max)
5: DECLARE @SQL nvarchar(max)
6:
7: DECLARE extensionViews CURSOR FOR
8: -- Get all views within the database
9: SELECT [name] As ViewName
10: FROM sys.views
11:
12: OPEN extensionViews
13:
14: FETCH NEXT FROM extensionViews
15: INTO @ViewName
16:
17: -- Check @@FETCH_STATUS to see if there are any more rows to fetch.
18: WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
19: BEGIN
20:
21: -- Build the dynamic SQL for updating the view on the fetched row
22: SET @SQL =
23: 'IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sysobjects WHERE type = ''V'' AND name = ''' + @ViewName +''')
24: BEGIN
25: exec sp_refreshview N''dbo.'+ @ViewName + '''END'
26:
27: exec(@SQL)
28:
29: -- This is executed as long as the previous fetch succeeds.
30: FETCH NEXT FROM extensionViews
31: INTO @ViewName
32: END
33:
34: CLOSE extensionViews
35: DEALLOCATE extensionViews
36:
37: GO
Hope you find a use for this!
Greg Olsen
Yellow Duck Guy
SQL Reporting Services – Easy Date Function
Sometimes I use this simple but effective date function in my reports (NZ reports) by using the ‘Code’ functionality given by SQL Reporting Services. Therefore I thought I would paste this on my site for quick reference. Feel free to use.
Public Function FormatDate(ByVal d As Date)
Return d.ToString("dd/MM/yyyy")
End Function
To find where to paste your code then simply goto ‘Report Properties’ from the Report Menu (in Report Designer) and select the ‘Code’ tab. Then paste your code inside the window made available and click OK.
Then to use in your reports, simply call it like the following …
=code.FormatDate(Fields!DATE.Value)
The function above also illustrates how you can write your own functions and call them within your report.
If you are ever wondering where your code will be stored then have a look inside your RDL (report exension .rdl) report file and search for the XML tags of <CODE></CODE>. You will notice it inside there.
Simple aye! Happy coding.
Yellow Duck Guy
Greg Olsen
Options for Creating SSRS Reports
There are 2 options for creating Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services Reports:
- Report Builder
- Report Designer
Report Builder
Microsoft hasn’t forgotten the end user i.e. your Business Analyst. SQL Server is shipping with an end-user reporting tool right in the box. Report Builder is a ClickOnce Windows Forms application that users download from the report server to their local computer.
That means that end users install it from the Web browser, but once installed it’s not a browser-based application. To get started with Report Builder, browse to your Reporting Services home page. This will have a URL something like http://YellowDuckGuyServer/Reports (or http://localhost/Reports if you’re running the browser (within IIS) on the same box with SQL Server 2005 itself – sometimes common where starting out!). Next you will need to click the Report Builder link in the home page menu bar to install and launch Report Builder. The Report Builder will load with the New Report dialog box, showing all the available report models. I suggest you try this out if you want to get started with the Report Builder. Your DBA will need to do a bit of setup before your end users can create their own reports. Your end users also will need to know about their data also in order to design useful reports.
Users create reports within the Report Builder by simply dragging fields from the predefined report models onto a pre-designed report layout template. Users can format, group and sort, and filter their data. In addition, they can edit or define formulas. With Report Builder, users don’t need to understand the underlying structure of the data source and they don’t need to understand any complex computing languages. They simply need to be familiar with the data in their data sources.
Report Designer
Report Designer is the tool I use the most when designing reports and is focused towards your developers. You can use Report Designer within Visual Studio after installing Reporting Services on your machine or simply the Report Designer. I’m currently using SQL Reporting Services 2005 with Visual Studio 2005.
Expression Builder within Report Designer used to create report expressions is written in VB or something close to it so your VB developers out there will love it!
So your developers (that includes me!) will use Report Designer to create more complex reports. You have complete control over the layout, and you can add advanced features such as expressions, custom assemblies that run from the report, and report interaction for drilling down or linking to related data. You can also create basic reports that consist of simple tables, matrix, image, or lists.
In Report Designer, you can create a report in three ways.
- You can create a blank report and build your report from scratch – I recommend this option.
- You can use Report Wizard, which automatically creates a table or matrix report based on information you provide. This option I would not recommend if you really want to learn best practices with report building.
- You can also import an existing report from Microsoft Access.
Reports are published to a report server as Report Definition Language (RDL). files as I slightly mentioned in my previous SSRS Yellow Duck Guy posting. Because a report definition is an XML document, you can create and edit reports using anything you like that can attack an XML file i.e. XML Notepad.
Under the hood, Report Designer uses the Reporting Services Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) API to publish reports to a report server. You also have the option to upload reports using Report Manager on the report server (this could also be on your local machine).
Well now you should know the options available for building reports with SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS).
Yellow Duck Guy
Greg Olsen